A Comprehensive Guide to Payroll Management
Payroll management isn't just an annual salary divided by 12 months. It is so much more than that.
There are tax deductions, reimbursements, Provident Fund (PF) and Employee State Insurance Scheme (ESI) calculations, estimations of attendance and leaves, and more!
In recent months, we have had discussions with numerous Indian startup founders and HR professionals. Many of them still use spreadsheets and manual processes to manage their operations, leading to frequent errors in payroll calculation, delays in salary processing, and overall employee dissatisfaction.
If you are building payroll operations from scratch in your organisation, you have to read this guide. We will cover everything about payroll management and processing, including stages, components and best payroll management solutions. Our focus will be specifically on the Indian context.
Without further ado, let’s get started
What is Payroll?
Payroll refers to the total amount an employer pays their employees. But that’s possibly the textbook definition of payroll. In reality, there are lots of elements involved in a payroll.
In reality, a successful payroll function is the summation of multiple sub-functions such as:
Clearly defining the payroll components such as PF, ESI, house rent allowances (HRA), Flexi-benefits plan components, allowances and reimbursements
Integrating payroll with employee leaves and timesheets to ensure that employees are correctly compensated
Processing payroll at the right time and through a secured process to protect organisations’ and employees’ privacy
Preparing and releasing relevant documents such as payslips, tax deduction statements
What are the Stages in Payroll Processing?
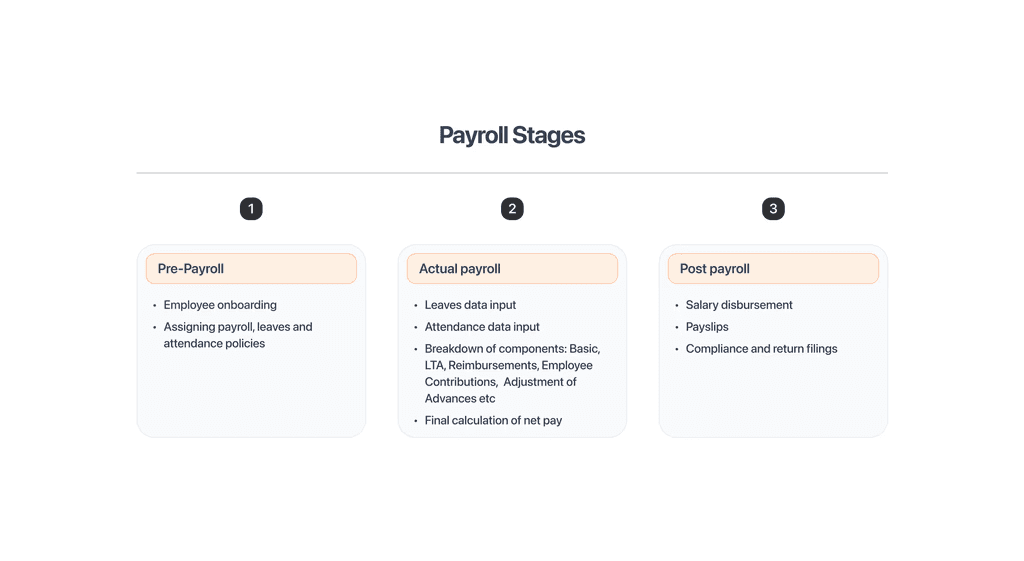
Payroll processing refers to the steps involved in calculating and processing your employees' payroll. Payroll processing involves three distinct phases:
Pre-payroll activities: In this stage, the HR and finance teams onboard employees and create payroll policies, gather inputs and validate the inputs before calculating the salaries of each employee
Actual payroll process: The goal of this stage is to calculate the payroll of individual employees based on payroll policy, their respective salary packages, tax slabs, deductions, exemptions and reimbursements. Rolling the payouts is also part of this stage.
Post-payroll activities: This stage is about conducting payroll reporting and releasing payroll documents like payslips and tax certificates. Statutory Return Filings such as PF, ESIC, PT & TDS are part of this step.
Pre-Payroll Activities
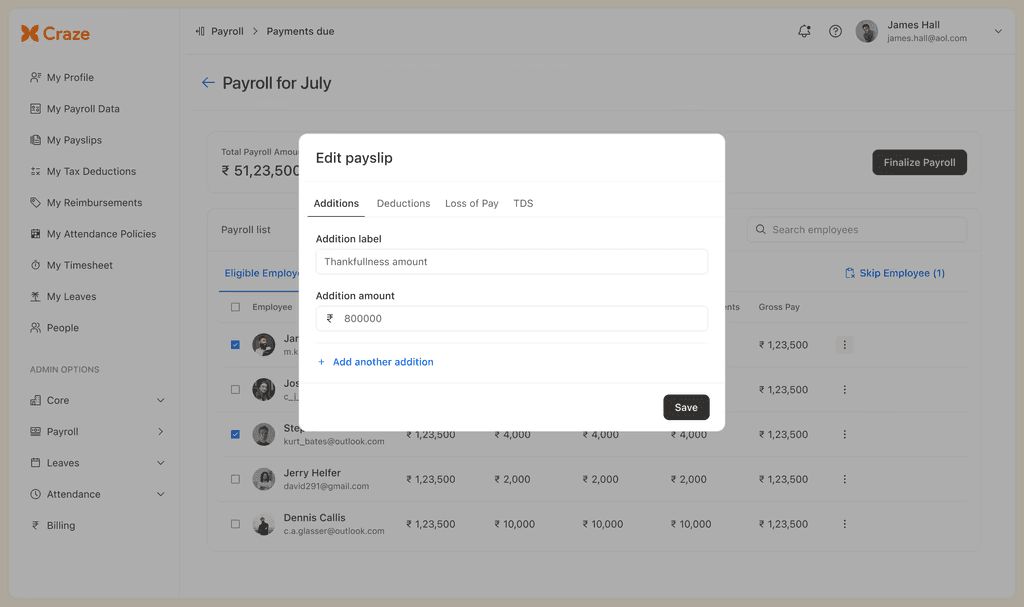
Pre-payroll activities include deciding each employee's salary components and finalising their gross pay. This could be as simple as dividing their annual compensations by 12. However, additional factors, such as performance bonuses, reimbursement requests, and loss of pay, are also involved.
The types of data you will require to input for this stage are:
Employee attendance and leave balance
Payment information including salary, bonus, reimbursements, allowances
Actual Payroll Process
Once each employee's gross pay is decided, it is time to calculate their actual salaries. This step involves calculating the taxes that each employee is eligible for and deducting them from their gross pay to reach net pay (the amount employees secure at their bank every month). The most common types of tax and other deductions in the Indian context include Income Tax, Provident Fund, Employee State Insurance, and Professional Tax. Apart from these, company-specific insurance policies and loan repayments also account for deductions from gross pay. The typical payroll calculation is as follows
Net pay = Gross Pay - Deductions Here: Gross Pay = Basic Salary + House Rent Allowance + Allowances + Reimbursements + Arrears + Bonus
Deductions = Professional Tax + Employee Provident Fund + Income Tax + Insurance + Leave adjustments + Loan repayments (if any)

Post-Payroll Process
The post-payroll process involves three steps:
Payroll accounting
The goal of the payroll accounting stage is to record all transactions, such as employee compensations (gross and net), payroll taxes, health insurance and other benefits, providend fund contributions (employer and employee), paid leaves, etc. Before rolling out the payroll, you must record everything within your accounting system for future reference.
Payout
Once you have accurately calculated the pay of all employees and recorded them within the system, you can run the payroll. You can do this with payroll software like Craze, which allows payroll data validation, calculation, compliance, and processing to happen simultaneously. Just click ‘Process Payroll’, and you are ready.
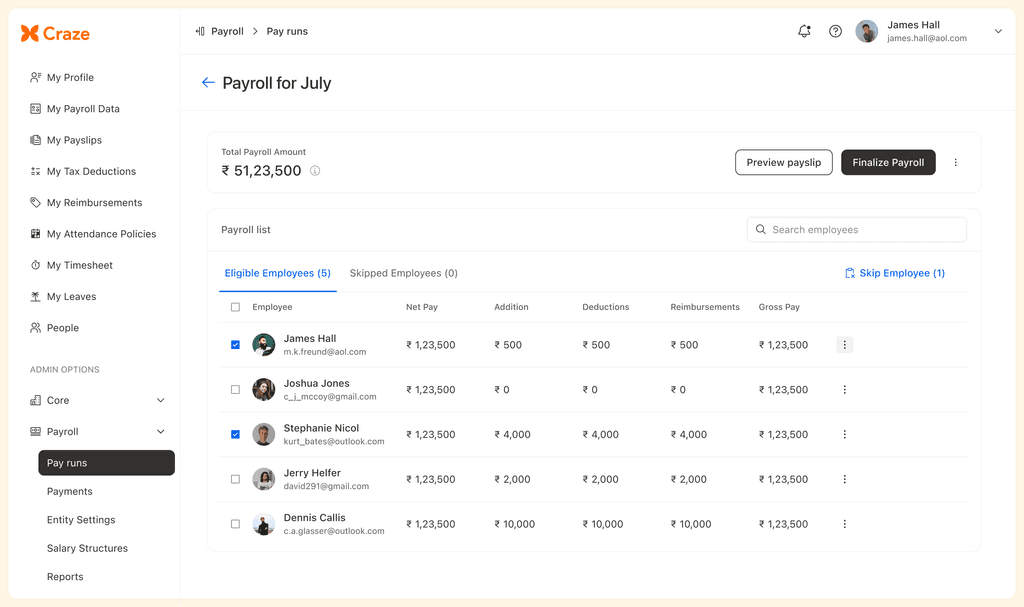
You can process payroll outside of payroll software by logging into the bank's CMS and making bulk or individual payouts via the bank advice file.
Payroll reporting
The finance team must create a report after the monthly payroll is rolled out. The purpose of this report is to communicate employee costs and department-specific costs with the C-suite. Additionally, generating tax deducted at source (TDS) reports and payslips and providing fund challans and other compliance reports are also part of this step. You can create this manually or opt for payroll software that automates the entire reporting stage.
What are the Components of Payroll?
Payroll components don’t have to be the same for each company. However, to stay compliant with the Indian legislations and tax laws, certain components must be part of your organisation’s salary structure, including:
Basic salary
Allowances
Deductions
Gross and net salaries
TDS
Other taxes
Bonus
Benefits
A typical payslip of an Indian company looks something like this 👇
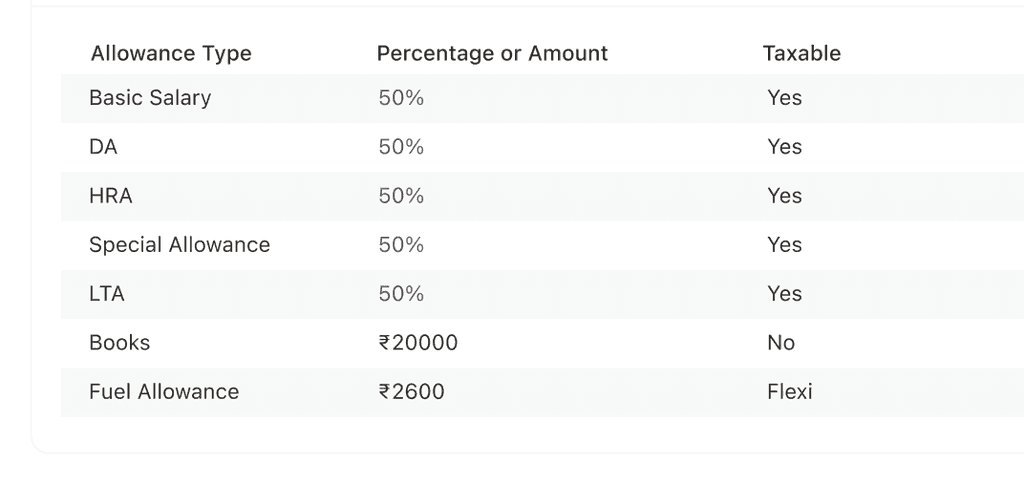
Let’s learn more about each of these components in detail:
Basic salary: The basic salary is a fixed, pre-decided amount that varies for each employee. It is usually decided based on an employee’s experiences and expertise. It is the salary component in an employee’s payslip without adding the allowances, bonuses, or tax deductions.
Allowances: Allowances are salary components that employees receive over and above their basic salaries. While allowances depend on an employee’s eligibility and the employer’s salary structure, a few common allowances are part of most Indian salary payslips. These include HRA, leave travel allowances (LTA), overtime allowances, etc.
Bonus: A bonus is more of an ad-hoc payment or an additional amount beyond an employee’s regular paycheck. It can be one-time, monthly, quarterly, half yearly or a custom amount that an employee receives as a reward for exceptional performance or for referring an expert who gets hired in the same company. Bonuses are taxable.
Deductions: Deductions are the compensation components subtracted from an employee’s gross salary before arriving at their net salary. These include tax deductions, benefit deductions (medical insurance), employee provident fund, TDS, loan repayments, etc.
Benefits: Benefits include food cards, gym memberships, car and phone recharge and so on.
Gross and net salaries: Gross salary is the summation of basic salary, allowances, benefits and bonuses. Net salary is the salary you have at hand after deducting tax and other components.
What are the different Payroll Processing Methods?
Did you know that the terror of not processing accurate payroll within time often gives sleepless nights to founders and HRs? We have talked to too many of them to confirm this. 😎
Jokes apart, here are the different payroll processing methods to make HRs’ lives easier:
Manual payroll processing via spreadsheet
Under this method, organisations maintain their employee database within a spreadsheet. They use a set formula to calculate the entire team’s salaries. Once the salaries are estimated, the finance team manually transfers each employee's wages by logging into the bank CMS. In some cases, organisations also hand over cheques to the employees that they need to withdraw from the banks.
Pros: The only benefit of this method is that it is cost-effective.
Cons: This payroll processing method is only feasible for very small companies with few team members. It is not scalable, as you cannot add personalised salary components to it. The database can crash if you want to include more employees in your payroll or add new deductions.
By using HR payroll services
This means outsourcing the entire payroll function to an agency or service provider. You provide the agency with relevant employee data, attendance, and salary information, and they are responsible for calculating and rolling out your payroll.
Pros: You don’t need to handle the headache of calculating payroll and staying compliant.
Cons: Multiple coordination and privacy issues as you trust an outside company with your confidential information.
By using payroll software
Payroll software is an end-to-end automation tool that takes over your payroll operations right from onboarding. As you insert initial data like employee information or integrate this software with your existing workplace software, it extracts all related details, creates centralised employee hubs, integrates with an attendance management platform, and auto-calculates compliant, accurate payroll. Not only that, but you can also process payroll from this software without signing into the bank server. It also generates payroll reports, payslips, and tax certificates and empowers employees to download these relevant documents from a self-serve platform.
Pros: Everything! You have all the stages of payroll automated without any security concerns.
Cons: Nothing that we can think of. Can you? 😎

Challenges in Payroll Management
Payroll management is not a bed of roses. And by now, you have probably already realised that. Here are the most common challenges that you may encounter when running a payroll system end-to-end:
Balancing manual and automated systems
The biggest challenge you will face is balancing automated and manual systems. Relying entirely on manual systems would mean errors in payroll, back-and-forth calculations, and no integration with the attendance system. It's like a ticking bomb, and your entire system may collapse with many formulas and inputs. Similarly, if you opt for a semi-automated payroll system, the biggest confusion is related to which parts to automate. Many times, organisations simply automate the most straightforward parts and end up performing critical manual activities like invoice approval, manually inputting employee attendance, etc.
Finally, fully automated payroll software is not always the best. Most of these tools have integration issues. Unlike Craze, they don’t auto-sync with attendance and leave management software, leading to errors in payroll calculation.
Keeping up with compliances
There are way too many payroll compliances and tax slabs to remember. For a single person, remembering and applying these compliances is next to impossible. But you will be subject to legal trouble and penalties if you don't.
Protecting sensitive employee data
With data infringement incidents happening worldwide, ensuring your payroll process is end-to-end protected takes extra effort. You are dealing with employees’ sensitive information and your company's financial data. There is no room for taking risks.
Processing payroll for remote teams
If your entire team or parts of it are remote, it is a huge challenge to process all of their salaries at once. This is especially true if they are from different states and countries and are accepting salaries in multiple currencies.
Processing payroll for employees and contractors
Most companies today work with freelancers, independent contractors, and consultants. When it comes to processing payroll, you need a platform that can process all of their payroll at once. Too many systems complicate the entire HR payroll process, leading to delays and errors.
Best Payroll Software Solutions for SMEs & Startups
If you are looking for a secure and automated payroll management system, here are our recommendations:
Craze

Craze is the perfect payroll software for startups and SMEs. It is fast (you can run payroll in a few hours), compliant, and has an extremely empathetic support team that’s always ready to help.
Some of the best payroll features of Craze include:
Automated, error-free payroll calculation and one-click payments to process payroll from within the software
A self-serve HR software dashboard where employees can download payslips, and tax receipts without the HR or finance team’s involvement
All-in-one dashboard to process both employee and contractors’ payments
A unified admin system that includes HR, payroll, attendance, and leave management software to create a connected system
Price
Core HR: ₹40/employee/month (mandatory)
Payroll: ₹60/employee/month with access to all advanced features
Feel free to contact the team for enterprise plans and personalised use cases.

RazorpayX Payroll
This fully automated payroll management software has features like automated tax filing, compliance, and salary deposits. However, this software doesn’t offer a connected experience, and the pricing plans start from ₹2999/ month for 20 employees, which is costly for startups.
Read detailed RazorpayX Payroll Review.
KekaKeka’s
automated payroll system and rule-based salary components help organisations process compliant salaries without legal knowledge. However, the pricing plan starts from ₹9,999/month, and access to advanced payroll features is limited.
Read detailed Keka Review.
Statutory Compliances and Payroll Taxes in India
Some of the mandatory Indian statutory compliances and payroll taxes you should know are:
Payment of Wages Act, 1936
Minimum Wages Act, 1948
Maternity Benefits Act, 1961
Employees' State Insurance Act, 1948
Employees' Provident Fund Act, 1952
Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
Union Budget 24-25 Impact on Payroll
Here’s the summary of the changes from Union Budget 24-25 and it impact on payroll.
Payroll changes for employees
Tax slab revisions
Adjustments to standard deductions
TDS/TCS credit updates
Increased deductions for pensioners
Higher NPS deductions
No changes in the Old Regime
Payroll changes for employers
First time employees - First time formal sector employees having salary upto ₹1 lakh, to receive direct benefit transfer of one-month salary in 3 instalments as registered in the EPFO up to ₹15,000.
Support to employers - The government will reimburse to employers up to ₹3,000 per month for 2 years towards the EPFO contribution for each additional employment within a salary of ₹1 lakh.
Internship Opportunities - Companies will be able to transfer the internship costs and contribute 10 per cent of such cost through their Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) funds.
Rationalisation of TDS Rates
Future Trends in Payroll Management
Wondering which future trends to anticipate in payroll management in the coming years? Here’s how we are imagining it:
AI-integrated payroll: Automated payroll from payroll data validation, calculation, processing and report generation. There is no human involvement except in coordinating the entire payroll cycle.
Simple tools with clean user interface: Legacy payroll tools have clunky interfaces, making it difficult to navigate to the correct option. Today’s startups are more keen on finding simpler tools with neat interfaces that everyone can operate.
Integrated payroll experience: Gone are the days when you needed to integrate multiple tools or manage spreadsheets to sync payroll with core HR, leave and attendance management platforms. Companies are now looking for a single dashboard to keep a close tab on all HR, IT and finance operations.
Connecting gig economy: The gig economy culture is rising in India. Startups are now looking for payroll platforms to integrate freelancers and employees and process both invoices without any hassle.
Conclusion
Processing end-to-end payroll can be complicated and overwhelming, especially for startup founders with so much on their plates. Look for payroll software that makes your lives easier. With minimum to no involvement from your end, it should handle all finance and HR tasks.
And that brings us to our recommendation: Craze.
Craze is perfect for you if:
You are all set to build people operations in your company from scratch
You need an end-to-end automated payroll software that’s affordable and provides access to advanced features
You are seeking an empathetic support team that genuinely cares about your concerns
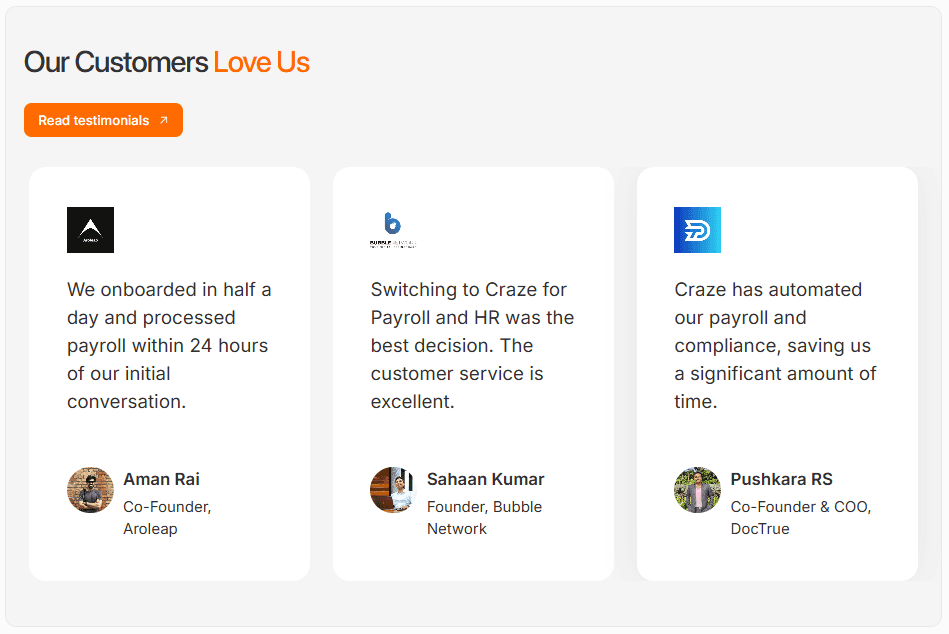
Craze customers say the same thing about it 👇

To see Craze in action

FAQs
What is payroll management?
Payroll management administers employee salaries, including calculating wages, deductions, taxes, and benefits. It involves pre-payroll activities, actual payroll processing, and post-payroll tasks like reporting and document generation.
What is a payroll management system?
A payroll management system is software that automates payroll processes, from employee data management to salary calculation and disbursement. It handles tax deductions and compliance and generates reports, streamlining the entire payroll function.
What is the difference between payroll & Salary?
Salary is the fixed amount an employee receives. At the same time, payroll encompasses the entire process of calculating and distributing compensation, including salaries, taxes, deductions, and benefits for all employees in an organisation.
Which software is best for payroll: Cloud-based or On-premise?
Cloud-based software like Craze is much more efficient and affordable.
What is the Formula of Payroll?
The basic payroll formula is:
Net pay = Gross Pay - Deductions
Where Gross Pay = Basic Salary + Allowances + Reimbursements + Arrears + Bonus
Deductions include taxes, provident funds, insurance, and other applicable items.
What are the benefits of using software for payroll?
Payroll software automates calculations, ensures compliance, reduces errors, saves time, integrates with other systems, provides employee self-service options, generates reports automatically, and enhances data security and privacy.
